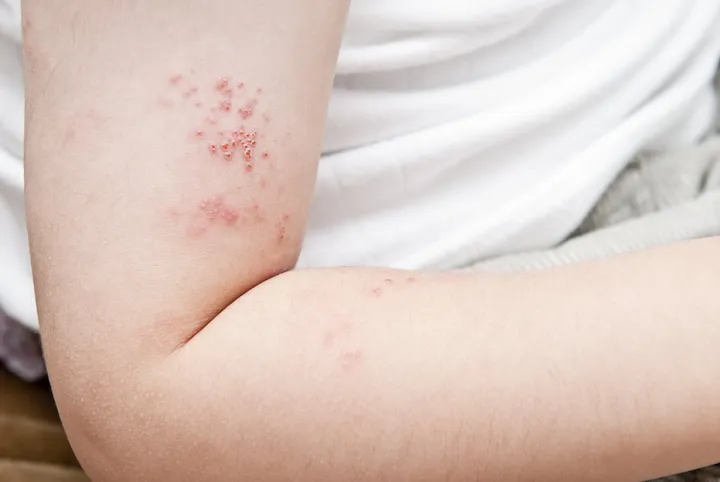
Skin infections occur when harmful microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites invade the skin and cause inflammation. These infections can range from mild to severe and can affect any part of the body. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial to prevent complications and promote healing.
A skin infection is an infection that affects the skin’s layers, caused by microorganisms like bacteria (e.g., Staphylococcus aureus), viruses (e.g., herpes simplex), fungi (e.g., ringworm), or parasites (e.g., scabies). Common types of skin infections include cellulitis, impetigo, fungal infections, viral warts, and scabies.
Diagnosing and treating a skin infection typically involves the following steps:
While nebulizers are used for respiratory conditions, skin infections are typically treated with other methods, including:
Understanding the causes and treatment options for skin infections helps individuals manage their condition effectively, adhere to prescribed treatments, and take preventive measures to maintain skin health.
© 2021-2025 Jackson Urgent Care. All Rights Reserved. Made With Love by Ignite Marketing Agency.