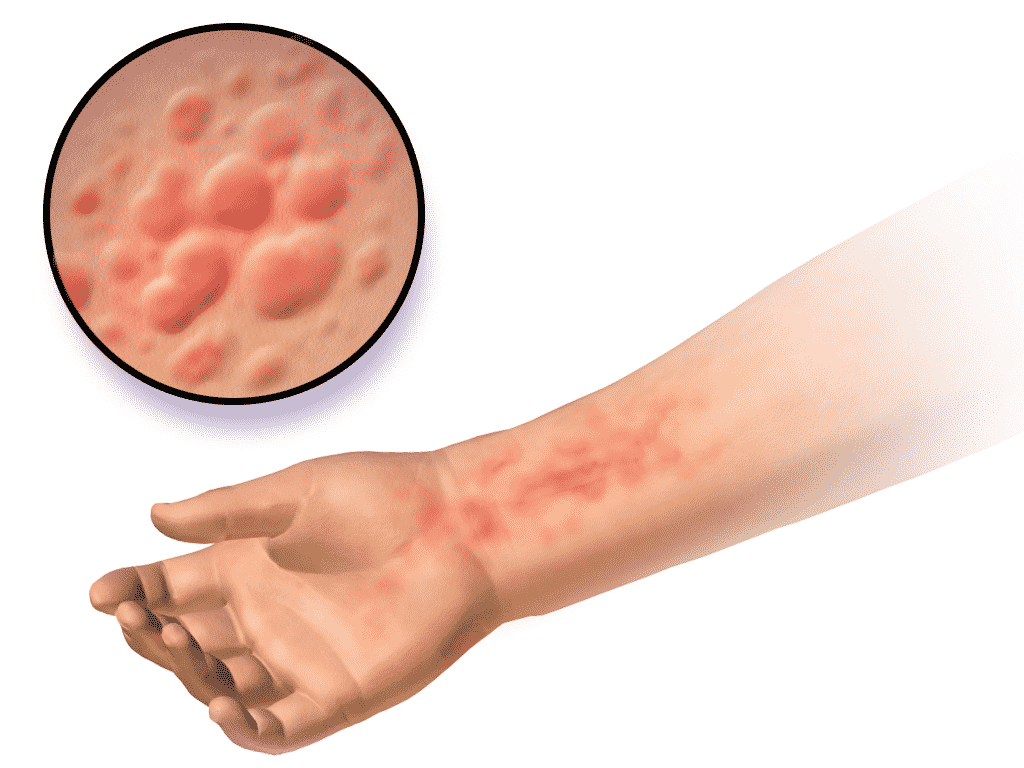
Hives, also known as urticaria, are raised, itchy welts on the skin that can vary in size and appear anywhere on the body. They are usually red, pink, or flesh-colored and can cause significant discomfort. Hives can be triggered by various factors, including allergies, infections, stress, and certain medications. Understanding the causes and treatment options […]
Hives are a common skin reaction characterized by the sudden appearance of swollen, pale red bumps or plaques (wheals) on the skin. They can last for hours or days and may recur over a longer period. Hives are often the result of an allergic reaction, but they can also be caused by non-allergic factors such as physical triggers (heat, cold, pressure), infections, stress, or underlying medical conditions.
Diagnosing and treating hives typically involves several steps:
Nebulizers are used for respiratory treatments, while hives are managed with different methods, including:
Understanding the causes and treatment options for hives can help individuals manage their condition effectively, reduce symptoms, and improve their quality of life. If hives persist or are accompanied by severe symptoms such as difficulty breathing or swelling of the face and throat, seek immediate medical attention.
© 2021-2025 Jackson Urgent Care. All Rights Reserved. Made With Love by Ignite Marketing Agency.