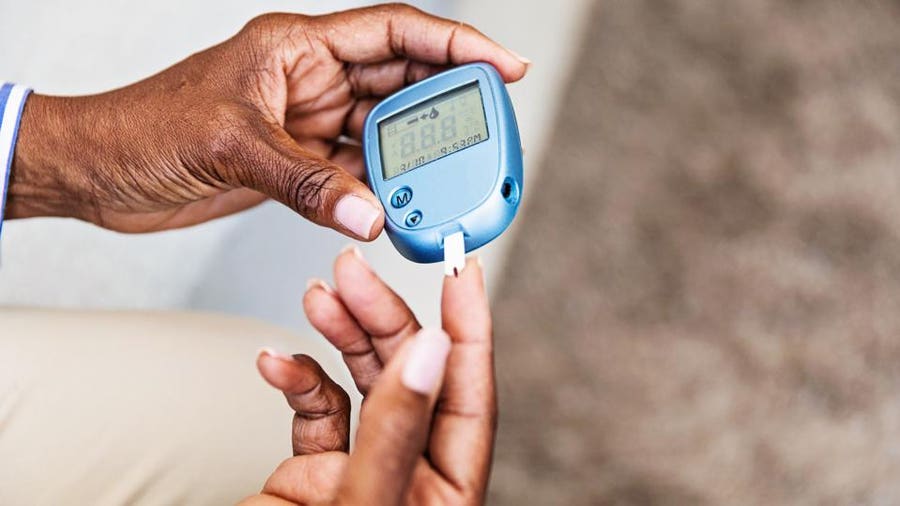
A glucometer, also known as a blood glucose meter, is a medical device used to measure the concentration of glucose in the blood. It is a vital tool for individuals with diabetes, allowing them to monitor and manage their blood sugar levels effectively.
A glucometer is a portable device designed to measure blood glucose levels quickly and accurately. It consists of a lancet for pricking the skin to obtain a small blood sample, test strips to collect the blood, and a digital meter that reads and displays the glucose level.
The process of using a glucometer typically involves the following steps:
© 2021-2025 Jackson Urgent Care. All Rights Reserved. Made With Love by Ignite Marketing Agency.