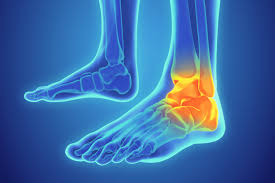
Sprain injuries occur when ligaments, the tough bands of fibrous tissue that connect bones, are stretched or torn. This can happen due to a sudden twist, fall, or impact, commonly affecting the ankles, wrists, and knees. Proper treatment and rehabilitation are essential for recovery and to prevent further injury.
A sprain is an injury to a ligament caused by being stretched beyond its normal range of motion, resulting in a tear. Sprains are classified into three grades:
The treatment procedure for sprains typically involves:
While nebulizers are not relevant for sprain injuries, alternative treatments and aids include:
By understanding sprain injuries and following appropriate treatment protocols, you can ensure effective healing and minimize the risk of complications and recurrence.
© 2021-2025 Jackson Urgent Care. All Rights Reserved. Made With Love by Ignite Marketing Agency.